Utillization of Green Betel Leaves (Piper betle L) as Traditional Medicine for Local Commununities in Serang Jaya Hilir Village, Pematang Jaya, Langkat
Pemanfaatan Daun Sirih Hijau (Piper betle L) Sebagai Obat Tradisional Bagi Masyarakat Lokal di Desa Serang Jaya Hilir, Pematang Jaya, Langkat
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32938/jbe.v10i2.9570Keywords:
Utilization; Green betel leavis (Piper betle L); Tradisional medicine; Etnobotany; Serang Jaya Hilir VillageAbstract
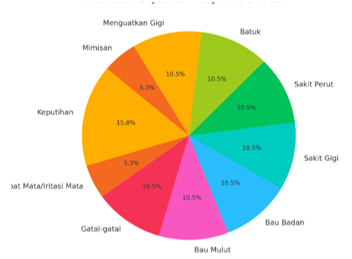
Indonesia is a center of biodiversity, including the green betel plant (Piper betle L) which has long been used in traditional traditions and medicine. This study aims to identify the use of green betel leaves, the types of diseases treated and the processing methods as traditional medicine by local people in Serang Jaya Hilir Village, Pematang Jaya District, Langkat Regency. The study was conducted in four hamlets of Serang Jaya Hilir Village with a qualitative research type using a quantitative descriptive method. In this study, the selection of respondents was carried out using the purposive sampling method, meaning that the data taken was based on community understanding related to the use of green betel leaves as traditional medicine, consisting of 10 respondents. The data is presented in the form of tables and graphs with data collection techniques in the form of observation, interviews, and documentation. The results of the study showed that people use green betel leaves to treat 10 types of diseases, including vaginal discharge, eye irritation, itching, bad breath, body odor, toothache, stomachache, cough, strengthening teeth, and nosebleeds. The method of processing and using betel leaves varies according to the type of disease, such as boiling, chewing, pounding, or rolling. Leucorrhea is the most frequently mentioned complaint, indicating public trust in the effectiveness of green betel leaves in traditional medicine. This study is important as education regarding the safe use and preservation of green betel leaf resources so that they remain sustainable. Suggestions, the need for further scientific studies on the active content, and side effects of green betel leaves, as well as innovation of processed products so that their use is safer and wider.
References
Arsad, N. H., Putra, N. R., Idham, Z., Norodin, N. S. M., Yunus, M. A. C., & Aziz, A. H. A. (2023). Solubilization of eugenol from Piper betle leaves to supercritical carbon dioxide: Experimental and modelling. Results in Engineering, 17, 100914.
Atiya, A., Salim, M. A., Sinha, B. N., & Ranjan Lal, U. (2020). Two new anticancer phenolic derivatives from leaves of Piper betle Linn. Natural Product Research, 35(23), 5021–5029.
Daeli, D. Y. (2023). Studi etnobotani tanaman obat tradisional pada masyarakat di Desa Orahili Kecamatan Sirombu Kabupaten Nias Barat. Tunas: Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi, 4(1), 1-16.
Destriana A, & Ismawati I. (2019). Etnobotani and The Use Of Wild Plants as Traditional Medicine By The Madura Community.Journal of Food Technology and Agroindustry, 1 (2), 1-8.
HChowdhury, U. K., & Baruah, P. K. (2020). Betelvine (Piper betle L.): A potential source for oral care. In Current Botany (p. 87). Society for Scientific Research. https://doi.org/10.25081/cb.2020.v11.6130
Hulu, L. C., Fau, A., & Sarumaha, M. (2022). Pemanfaatan daun sirih hijau (Piper Betle L) sebagai obat tradisional di Kecamatan Lahusa. TUNAS: Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi, 3(1), 46-57
Khotimah, K., Nurchayati, N., & Ridho, R. (2018). Studi etnobotani tanaman berkhasiat obat berbasis pengetahuan lokal masyarakat Suku Osing di Kecamatan Licin Banyuwangi. Jurnal Biosense, 1(01), 36-50.
Kusuma, IW, & Sari, DP (2020). Pemanfaatan Tanaman Obat Tradisional di Masyarakat Desa . Jurnal Etnobotani Indonesia, 15(2), 123-134
Rahman, A., & Putri, L. (2019). Kandungan Kimia dan Khasiat Daun Sirih (Piper betle L.) sebagai Antiseptik Alami. Jurnal Farmasi Herbal , 8(1), 45-52.
Sahu, C., Balan, A., Bayineni, V. K., & Banerjee, S. (2021). Study of physicochemical and antioxidant synergy efficacy of betel leaf dried paste powde. In Croatian Journal of Food Science and Technology, (Vol. 13, Issue 2, p. 155). Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek, Faculty of Food Technology Osijek. https://doi.org/10.17508/cjfst.2021.13.2.03
Sari, M., & Hidayat, R. (2018). Studi Etnobotani Daun Sirih Hijau di Wilayah Pesisir Sumatera Utara. Jurnal Biologi Tropis , 10(3), 200-210.
Sonphakdi, T., Tani, A., Payaka, A., & Ungcharoenwiwat, P. (2024). Antibacterial and toxicity studies of phytochemicals from Piper betle leaf extract. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 36(10), 103430.
Supriadi, S., Suryani, S., Anggresani, L., Perawati, S., & Yulion, R. (2021). Analisis Penggunaan Obat Tradisional Dan Obat Modern Dalam Penggunaan Sendiri (Swamedikasi) Oleh Masyarakat. Jurnal Kesehatan, 14(2), 138-148.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 BIO-EDU: Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The Authors submitting a manuscript do so on the understanding that if accepted for publication, the copyright of the article shall be assigned to BIO-EDU: Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi and Departement of Biology Education, Universitas Timor as the publisher of the journal. Copyright encompasses rights to reproduce and deliver the article in all form and media, including reprints, photographs, microfilms, and any other similar reproductions, as well as translations.
BIO-EDU journal and Departement Biology Education, Universitas Timor, and the Editors make every effort to ensure that no wrong or misleading data, opinions, or statements be published in the journal. In any way, the contents of the articles and advertisements published in BIO-EDU are the sole and responsibility of their respective authors and advertisers.
Users of this website will be licensed to use materials from this website following the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


















